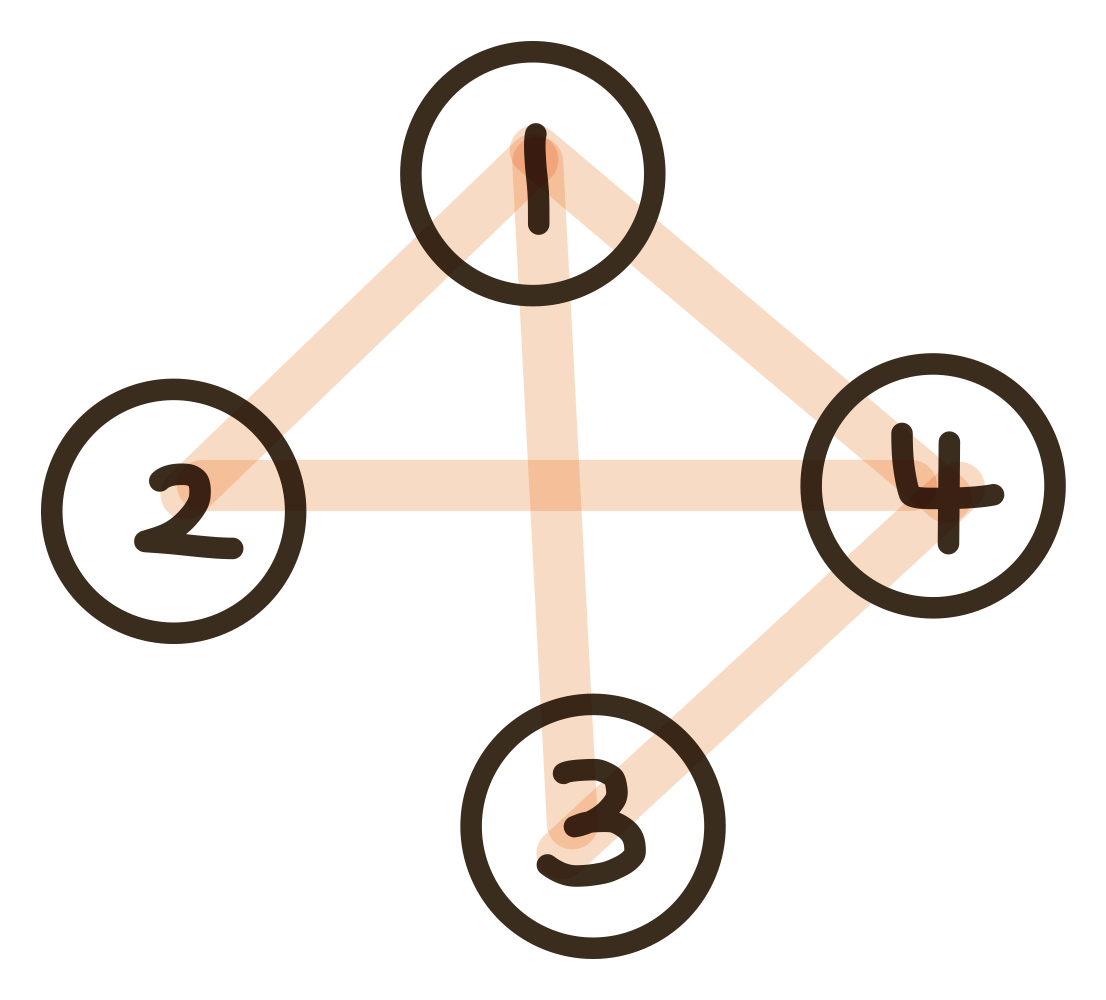
그래프를 탐색하는 방법에는 크게 **깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)**과 **너비 우선 탐색(BFS)**이 있습니다.
여기서 그래프란, 정점(node)과 그 정점을 연결하는 간선(edge)으로 이루어진 자료구조의 일종을 말하며,
그래프를 탐색한다는 것은 하나의 정점으로부터 시작하여 차례대로 모든 정점들을 한 번씩 방문하는 것을 말합니다.
아래의 그래프에서 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호를 1 이라고 가정하고 DFS, BFS 를 그림으로 설명하겠습니다.

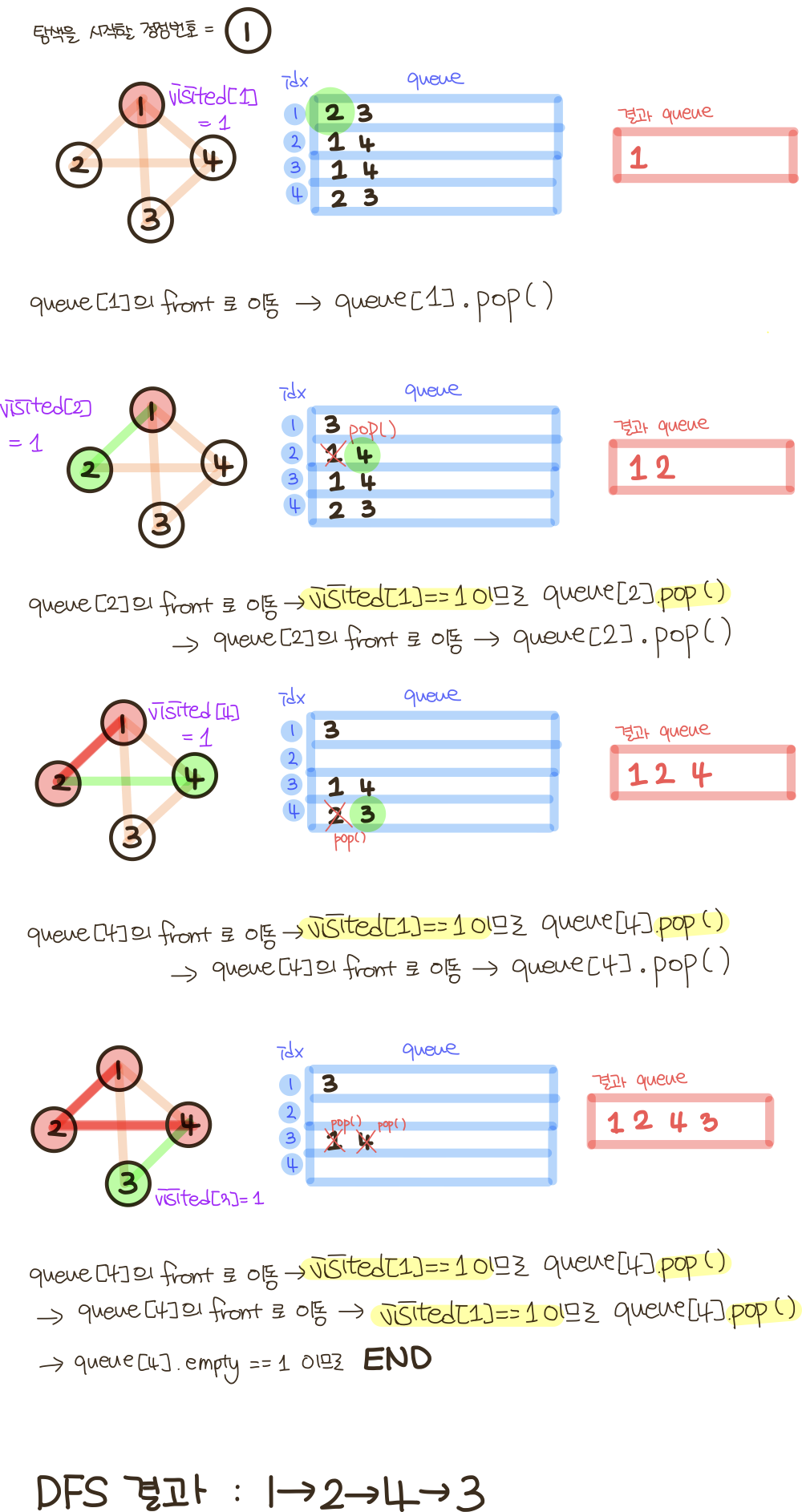
1. 깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS, Depth-First Search): 최대한 깊이 내려간 뒤, 더이상 깊이 갈 곳이 없을 경우 옆으로 이동 일반적으로 DFS 는 스택 또는 재귀함수로 구현합니다.
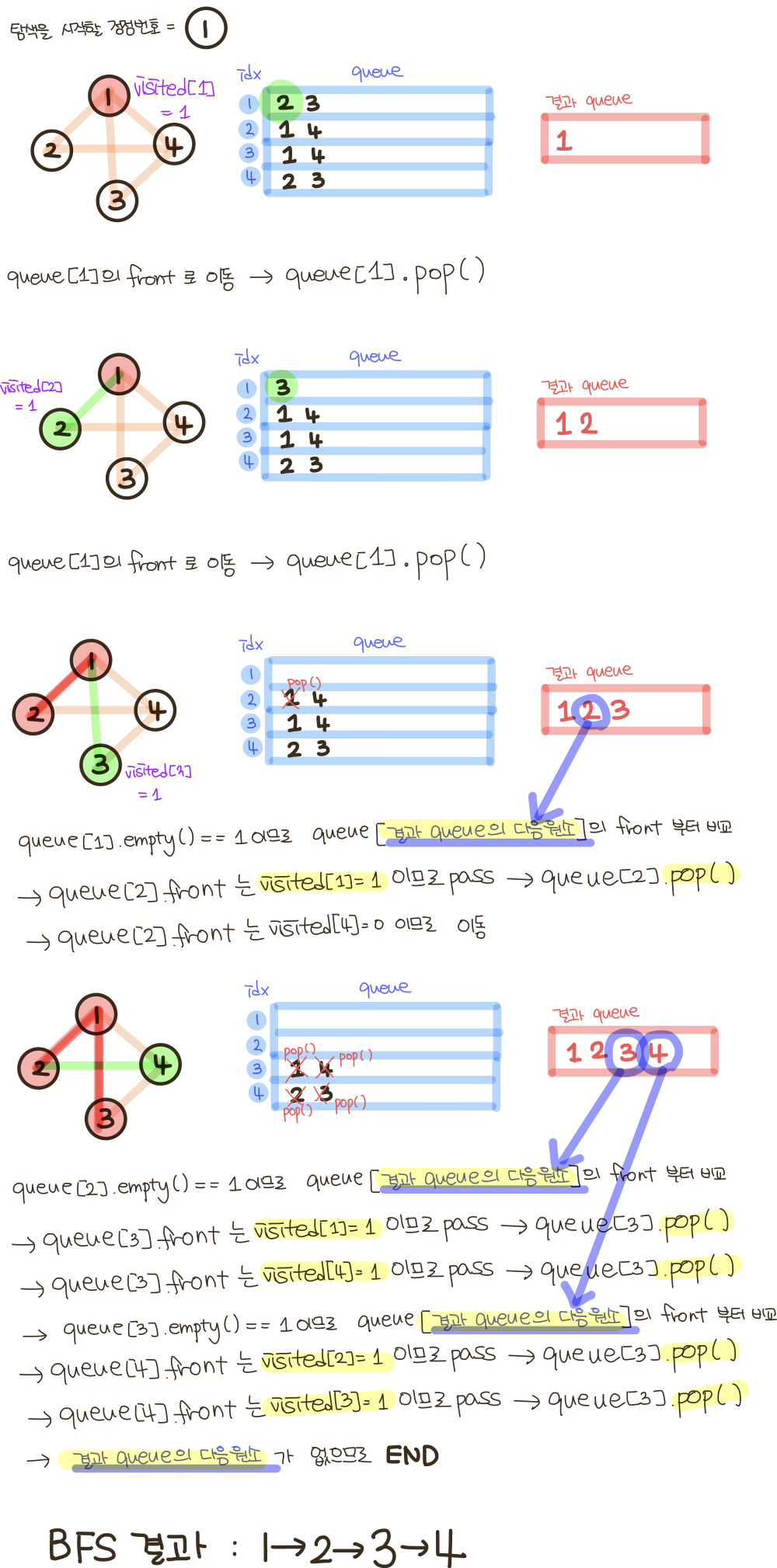
2. 너비 우선 탐색 (BFS, Breadth-First Search): 최대한 넓게 이동한 다음, 더 이상 갈 수 없을 때 아래로 이동 일반적으로 BFS 는 큐로 구현합니다
위의 그림을 코드로 나타낸 코드는 아래와 같습니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
void dfs(int start, std::vector<int> graph[], bool check[]){
check[start]= true;
std::cout << start;
for(int i=0; i < graph[start].size(); i++){
int next = graph[start][i];
if(check[next]==false){
dfs(next, graph, check);
}
}
}
int main (){
int n, m, start;
std::cin >> n >> m >> start;
std::vector<int> graph[n+1];
bool check [n+1];
fill(check, check+n+1, false);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int u,v;
std::cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
std::sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
dfs(start, graph, check);
cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
void bfs(int start, std::vector<int> graph[], bool check[]){
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
check[start] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << tmp;
for(int i=0; i<graph[tmp].size(); i++){
if(check[graph[tmp][i]] == false){
q.push(graph[tmp][i]);
check[graph[tmp][i]] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main (){
int n, m, start;
cin >> n >> m >> start;
std::std::cout << endl;vector<int> graph[n+1];
bool check [n+1];
fill(check, check+n+1, false);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
std::sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
bfs(start, graph, check);
std::cout << endl;
return 0;
}